Adwords Strategy Guide
from Dan Smith
imarketingtool.com
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Adwords is perhaps the best way for you to market your website on the internet.
-
Google Adwords will start sending your website traffic immediately. You don't have to wait to appear on organic search results.
-
Google will help you every step of the way. Google makes money by you participating in Adwords and wants you to succeed.
-
Adwords is the most powerful internet marketing tool currently on the internet. Adwords is a step (or two) above Yahoo Search Marketing
-
Most adwords campaigns are poorly maintained, making it possible for you get targeted traffic using the right strategy.
If you have never used Google Adwords, you can learn from Google. Visit the Adwords Home Page. Google will provide you with the basics of Adwords, including how to create campaigns and ad groups. This guide will show you to take Adwords beyond the basics.
Adwords Quality Score
First, Here is a video from the Chief Economist at Google on the importance of a good quality score.
Now that you know how important a Quality Score is, the question becomes how do you achieve a high score for you Adwords Ad. That is exactly what this guide shows you how to do.
You know CTR is the most important factor.
However, when you launch a campaign, you won't have impressions or clicks. Therefore, when you launch a new campaign, relevancy is the highest factor in your quality score.
Plus, you must pay for each click to get that good CTR. Keyword, ad and landing relevancy will keep that CPC as low as possible while you are building your CTR.
Relevance
The golden rule of Google Adwords is relevance. Google will grant you low minimum bids if you master the science of relevance. Without relevance you'll be paying too much per click and your competition will beat you in the market.
The google search engine is the undisputed search engine leader. Google beat out Yahoo, Altavista and MSN in the search engine market by building a better mousetrap. Google's search engine algorithm is a complex formula using many variables to return pages highly relevant to the search term used. The Google search engine is the best search for pages relevant to the search term. That's how they beat their competition. Relevance.
Google uses the same principal with Adwords. Advertisers with a message relevant to the search term are rewarded. Advertisers who are not relevant are allowed to compete, but they pay much higher rates per click.
Google determines relevance by two primary methods. The first is by examining each of you keywords and ads. Google checks the keyword, the ad headline and text, and the landing page to determine how relevant they are to each other. An automated program, or robot if you prefer, will crawl your landing page and determine if your page is relevant to the search term. A relevant page may only need to bid five or ten cents per click. A page not relevant will have to pay ten dollars in a competitive market.
The second method Google uses to measure relevance is the ads click through rate (CTR). Every time Adwords shows your ad to consumers, Google records that it gave your ad an impression. Every time a consumer click on the ad, Google records the clicks. The CTR is the number of clicks divided by the impressions. Adwords will assume that if consumers are clicking your ad frequently then the ad is relevant to the search term and will adjust the quality score upwards. Adwords will adjust the quality score down if the ad is not getting clicks. There will be more information on the CTR later.
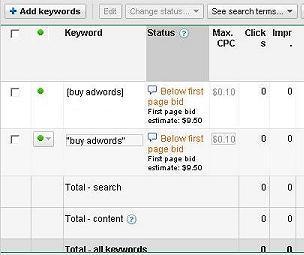
You can verify the keyword, ad and landing page relevance for yourself with an experiment. Take a competitive keyword and create an Adwords ad for it. For example, try buy adwords as your keyword. It's a great keyword to use because it has the word buy which pre-qualifies the searcher as willing to make purchase. Create an Adwords ad for it. What did Google set the first page bid at, five dollars, ten dollars or more?
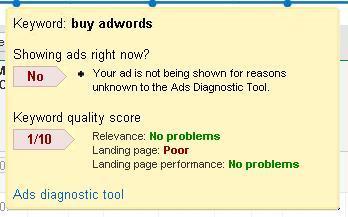
Adwords will tell you why you got such a high first page bid. The comment icon next to you keyword will give you diagnostic information. Adwords will tell you your quality score on a scale of one to ten. The quality score is how Google has scored the relevance of you keyword, ad and landing page. In this experiment, and in the example on the right, you have a poor quality score.
Adwords will event provide details of your quality score. Click on the details and recommendation link. Google will tell you your landing page is not relevant, and perhaps identify other problems.
You have just created poor ad. Go ahead and delete the ad group and campaign. You are not about to pay that much per click.
Start another Adwords experiment. Create a new campaign and a new ad group for buy adwords. Use only that keyword as a phrase match and exact match. Do not use the broad match. Do not use any other keywords.
This time, use the keyword buy adwords in the ad headline, and only this keyword. As you'll see later, having the keyword in the ad itself boost the quality score.
Use the landing page http://www.adwords-marketing-tool.com/buy-adwords/buy-adwords.aspx as the destination URL. The URL is complex, and for a specific reason, but more on that later. This is a customized landing page on this website, tailored for the keywords adwords marketing.
The landing page is now highly relevant to the keyword. Adwords rewards you with a lower minimum bid. The same keyword went from ten dollars per click to much lower. Stop and pick your jaw off the floor.
You may not get the same low first page bid or a 10 out of 10 quality score as in the screenshot. First, you are probably not using all the proper techniques in your ad. You'll learn all of those techniques in just a moment. Second, the campaign in the screenshot has an established CTR above 5% and sometimes above 10%, which assists the quality score. The ad you just created doesn't have any impressions or CTR.
You are now spending much less than you were with a poor ad. A reduction from ten dollars to ten cents is like paying one dollar for what you used to pay a hundred dollars for. The savings are amazing.
There are three main components to any Google Adwords ad. You'll want to examine each part of the ad. The parts of the ad are listed below.
- The keyword or phrase that triggers the ad to appear
- The landing page the ad will send the consumer to
- The actual text of the ad, or sales copy if you prefer
The key to the strategy is get all three parts of the ad working in harmony. A good keyword, a focused ad and a highly relevant landing page will get you a good or great quality score. A good quality score will allow you to bid very little for your keywords. You will be able to get traffic at a fraction of the cost to an uneducated advertiser.
There are two recommendations to get the most of your dollar when you begin the strategy. These rules will help manage the traffic and control your spending.
-
Disable the content network and search network option. You should only have the Google search option enabled. At first, you only want traffic from Google, not participating search engines or Adsense advertisers. Traffic from the search and content networks is low quality, so it will convert less. Disabling the search network and content network will help you control costs, at least until you have a proven ROI. Later you can come back and enable them if you choose. For now, you'll get plenty of traffic from Google.
-
Control your spending with the daily budget. When you start, you can decide what is the maximum per day you will spend with the daily budget. Your ads are no longer shown if the daily budget is exceeded, but it can protect you. It's important that you control your spending with the daily budget, and not your cost per click bid. If you set your CPC too low, you won't get a good ad position. Generally, you want you ad to be in one of the top three ad positions. You will not get many clicks if you are lower or off the first page. This lowers the CTR, which damages the quality score. In fact, making your CPC higher than you are comfortable with is a good tactic, as it should increase your CTR and quality score.
You are now ready to proceed with the Adwords Strategy.
The Keyword
You have probably visited the WordTracker keyword tool and Google Adwords keyword tool at some point in your internet marketing career. You would use these tools to generate a list of a hundred to a thousand keywords and phrases. You could use this list to create an Adwords campaign. Maybe you already have. This list of keywords has some value, so you'll want to retain it. But for now, you'll want to set it aside.
Instead you want to pick a single keyword or phrase to work with. You'll learn in the following steps how to create an Adwords ad and a landing page for just that one keyword. Google Adwords will recognize both your ad and landing page as highly relevant to the keyword.
One great aspect of Adwords is it lets you know instantly how well your ad is doing. Take a look at these two screenshots. The keywords are Adwords Profit and Buy Adwords. The internet marketing market is highly competitive.
You can view the quality score in Adwords from the keyword page by moving the mouse pointer over the caption icon. You'll notice it gives you a quality score from one to ten. This is where Adwords tells you how well your keyword, ad and landing page are working together. You are shooting for a good or great quality score for each an every keyword. Good quality scores begin at 8/10. These keywords have 10/10 quality score.
Paying five or ten cents for this keyword is not going to generate much traffic. You'll get more impressions if you bid higher, and more impressions means more clicks. But what you do have is the best of all possible starting points. Now that you have cheap traffic coming to your website, you concentrate on getting a return on your advertising investment. That ROI could come from a product, an affiliate program or perhaps even Adsense. Whatever the revenue generating means, you can now work on establishing a consistent ROI from your traffic. When you have that, come back to Adwords, increase your bid, get more impressions and traffic and let the money roll in.
You should have a good idea what keyword or phrase is good for your market. Ideally your keyword should be phrase, and the more targeted the phrase the less competition there is. Less competition usually means cheaper ads. However, you can go after the highly competitive keywords if you wish. The methods presented here will allow you to get the traffic for even a competitive keyword for the least amount of investment.
Suppose you still have you keyword list from Word Tracker and you want to find a good keyword from that list. Create an Adwords campaign for all those keywords under a single ad. Pay only 5 cents per click and don't be afraid to let Google disable most or all of the keywords (your ad won't be relevant to the keyword so you'll like get disabled quickly). Allow one week to pass and see which keywords are performing well for you. Adwords tells you how many impressions your ad made which represents how often someone searched for keyword. It also tells you the average position of your ad which represents how much competition there is. You would select a keyword from your campaign that has a high number of impression and a low average position. That would indicate a high search volume but low competition niche that you can dominate.
The Landing Page
Many ads on Google Adwords simply redirect a consumer to the default or home page. You do not want to do this. First, the home page is general not relevant to the keyword in question. Your landing page must contain the keyword, and feature the keyword prominently to be considered relevant by Adwords. Second, by targeting the landing page to the keyword, the consumer is likely to be more interested in your content. You must then persuade the consumer to make a purchase, click an ad other otherwise generate ROI.
You need to construct a landing page tailored for the keyword. Adwords will then consider the page relevant to the keyword and give you a high quality score. You accomplish that by addressing several pieces of a web page.
- The domain the page resides on
- The filename of the page
- The title of the page
- The page meta tags
- The content in <h1> tags
- The content of the page
The domain name of your website is important. You want the domain name to be in the general market for the keyword. Google Adwords considers the domain when assigning the quality score. Use hyphens in your domain name to separate individual words. This will assist Google in evaluating your domain name. For example, a good domain name for a website about the adwords marketing would be adwords-marketing-tool.com. The domain name contains the keywords adwords and marketing and they are hyphenated to make them readily apparent.
There is some debate to using hyphens in your domain name. On one hand the hyphens make it easy for Adwords and Search Engines to distinguish the individual keywords. On the other hand, human visitors tend to forget the hyphens and manually type Urls without them. The solution is simple. You should purchase both domains, with and without hyphens. You should use the hyphenated domain in all your marketing materials. But, you also have the domain without hypens should a visitor type your domain without them.
Domain names are only a few dollars for an entire year. There is no reason why you could not have both domains. In addition, you should have unique domains for every market you are selling to. Domain registration fees are very small when compared to your overall advertising budget.
Do not use a general domain name or have multiple pages selling to multiple markets. You want your website to only contain pages relevant to the market. When you create pages targeting unrelated keywords under one website and domain, the Google robots will identify all the various keywords. You will have diluted your website with many different unrelated keywords. Google will not consider your website relevant to any of the keywords. It will become difficult for your diluted website to get good quality scores for any keyword. Sell to only one market with your website, and make sure your domain is targeted to that market.
The name of your landing page should be the exact keywords you are targeting. You can name your Landing Page file anything you want. Why not make it the keywords the page is tailored for? Again, separating individual words with hyphens makes the keyword phrase easily apparent. For example, if the keyword is buy adwords, name your landing page file buy-adwords.htm. This accomplishes two things.
First, Adwords will recognize the keywords in the destination url. It's another opportunity to get you keyword in the Adwords ad. Every time you do, Adwords will boost the Quality Score.
Second, human visitors will also recognize keywords in the destination url and landing page url. It will help convince them that your landing page is the page they are looking for.
Your landing page should have the keyword as the title. Google Adwords considers the title of the landing page when assigning a quality score to your ad. The title of a page is set in the <title> tag with the <head> portion of the page. Please see the example code below.
<html>
<head>
<title>Buy Adwords at adwords-marketing-tool.com</title>
<meta name="keywords" content="buy adwords,google adwords,internet marketing"/>
<meta name="description" content="buy adwords information. Adwords ads too expensive? Save money with free guide."/>
...
</head>
<body>
<h1>Buy Adwords</h1>
...
</body>
</html>
Using meta tags in your landing page may make Google Adwords consider you page more relevant and get you a higher quality score. meta tags are also in the <head> portion of the page. Please see the example code.
You also want to use your keywords inside <h1> tags at the top of your page, just under the <body> tag. The Google Adwords robots will consider text with the <h1> tags to be important to the page. Traditionally <h1> tags are used to denote the title of the page within the content. Please see the example code.
Finally, you'll want the keyword to appear several times within the content of the landing page. Each time the Google Adwords robots identify the keyword in the content, Google will consider the page more relevant to that keyword.
All of these techniques should be familiar if you have used any Search Engine Optimization or SEO techniques. In both Google Adwords and SEO, Google will send a robot to examine the content of your page. The robots identify the keywords of a page by the same measurements. Any technique good for SEO should be good for Google Adwords.
What else can you do to boost your Quality Score? Assuming you've done the above, you've done the major things that go into a relevant landing page. There are also few other tactics that may increase your quality score. None of these are as important as the keyword tailored landing page.
(1) Have a link to your sitemap on your landing page. Google has said "Develop an easily navigable site." This means you need your landing pages to link to a sitemap of your website.
Normally, you don't want to give a consumer an alternative to taking your desired action (sign-up for your mailing list, buy a product, etc.) by having some other link on your landing page. The thought is that you only want to give the consumer one option, the option to take the desired action. But Google wants you to provide a way for the consumer to link to the rest of your website. In other words, Google wants you to have more than just a single landing page visible to the consumer. You still don't want much navigation on your website. But you can put a single link to a sitemap on your landing page. This link should be below the fold (down to where you'd need to scroll down to see it), preferably past your sales copy as the last thing on the page, perhaps in the footer portion of the page. Don't be afraid to make the font smaller as most footer links tend to be of a small font.
(2) Have a link to a "Privacy Policy" page and "Contact Us" page. Google states "Most internet users are concerned with understanding and controlling how websites use their personal information." Google wants you to be transparent, and inform your customers what you tend to do with their personal information. Create a page named "privacy-policy.htm" on your website, this will help Google identify it. Copy an existing policy from some other website and modify it for your website. Create a link to this page from your landing page. Again, put the link below the fold and at the end of your sales copy. You can use a smaller font for the link and put it in your footer.
Google also wants you to have contact page to make it easy for a customer to reach you. Name the page "contact-us.htm" to help Google recognize it. Include a mailing address, phone number and email address. Create a link to the page from your landing page.
If you want to take this tactic to the extreme, you might also try "Terms of Use", "Terms and Conditions", "About Us", "Shipping Policy" or "Return Policy" pages if applicable.
(3) Decrease your Page Load time. Google now considers page load time as a factor in the Quality Score. Remove unneeded elements to keep your page lean, and therefore fast. Don't have too many images, and make sure the one you have are relevant. Don't use too many javascripts or html code as that increases the page size and takes longer to load.
(4) Consider Geographic targeting. Google now reevaluates the Quality Score on every search. Part of the Quality Score is the geographic location, and Google will boost local merchants. Google knows the consumers IP Address and is able to tell the location from it. Appending city or state names to your keywords, and then tailoring ads and landing pages for your new keywords may increase you Quality Score. Plus, you could limit your campaign to your local area. This would diminish traffic, but it could boost your Quality Score.
All the techniques discussed so far are designed to get Google Adwords to consider your landing page a relevant page for your keyword, or to get a good quality score. You must also tailor your page to the consumer in order to a get Return of Investment or ROI for your advertising dollar.
Lastly, here is what Google has to say on the subject of landing pages. Google Landing Page and Site Quality Guidelines. Basically, you want your page to be relevant as the number one priority. You learned above how to make your page relevant. Beyond that, your website should be original, transparent and navigable. You also read information on those topics.
The Adwords Ad
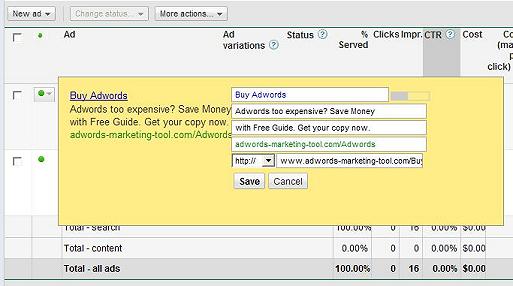
You'll want to treat your Adwords ad like sales copy. The ad is exactly that, sales copy meant to capture a consumers attention. The ad has three components.
- The headline
- Two description lines
- The URL
Your Adwords strategy is to make the keyword, the ad and the landing page work in unison. This will result in a high quality score and allow you to get highly targeted traffic to your website inexpensively. The perfect start is for you to use you keyword phrase as the headline of the ad. Imagine you have searched for a particular keyword as consumer. Several ads appear, but one ad contains the exact keyword you searched, while the other ads have few if any of you keywords. Which ads are you going to choose? The consumer is likely to choose the ad that most closely matches their search terms. In the example above, the keyword is buy adwords. Therefore, the headline of the ad is Buy Adwords.
The biggest component of maintaining a great quality score is having a good Click Through Rate or CTR. The CTR is the number of clicks the ad has generated divided by the number of impressions. The result is a percentage of consumers who have had your ad displayed and decided to click on it. The higher the CTR is the better. A high CTR means your ad is highly relevant and compelling to consumers. Google will adjust the quality score of your ad based on its CTR. A low CTR, under one half percent, will get your quality score lowered and could result in your ad getting disabled. You want a CTR of at least one half percent, perhaps even one percent. It is important for your ad to be relevant not only to the robots and programs at Google, but to consumers as well. This is the reason you should place your keyword in you ad headline.
Next you have two lines of 35 characters of sales copy for your ad. Many of the ads on Adwords today simply talk about the company or website running the ad. You do not want to do this. The cardinal rule of writing sales copy is that your advertisement must speak to the consumer. Good sales copy should promise to fulfill a want that the consumer has. It should speak to the consumer about a problem the consumer is looking solve. Describing your website or company rarely speaks to the consumer or fulfills a need. Don't waste any of the space talking about yourself, your company or your website.
To write good sales copy, you need to think like the consumer. The search term buy adwords would mean that the consumer is looking to purchase information on adwords. Your advertisement needs to convince the consumer that your website will provide that information.
You also want a call to action in your ad. A call to action is psychological tactic. People will often respond to instructions like click here now. You are directly telling the consumer to click on your ad. Google Adwords has banned a generic call to action like click here now. However, you can often craft a call to action that Google will accept, like Get help now and Find it here.
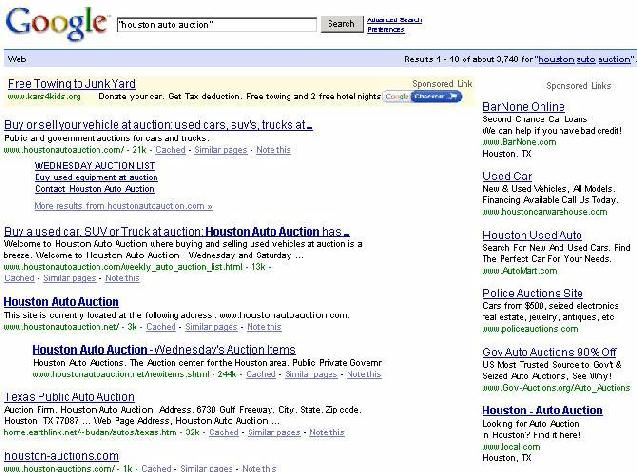
The following is a screen capture from Google of an actual search for the term Houston Auto Auction. Next, you'll see how relevant the adwords ads for this keyword are.
ly
The first Adwords ad that appears (on the top left of the page) is for donating your car to charity. This is complete unrelated to what you searched for. It is interesting to note that the since the website offer payments by Google Checkout, it gets an icon. That icon does make the ad stand out on the page, which is always a good thing.
The second Adwords ad that appears seems to be for car loans for people with bad credit. Perhaps you would be interested in this ad if you had searched for a car loan. Since you search for houston auto auction it is not very relevant at all. Apparently the business is located in Houston Texas, and Google added the geographic location at the bottom of the ad. Had the business been in another city, it's likely the ad would not have appeared at all.
The third ad is for used cars. This is related to auto auctions, but not very relevant to your consumers need. The domain name contains the word houston, and ad probably benefited from it.
The fourth ad is also for used cars.
The fifth ad is a generic auction website. This ad is in the ballpark, since it mentions cars and auctions. But it has a bunch of miscellaneous auction information as well. Worse, it doesn't mention Houston at all. You as the consumer have no idea what city or state this ad pertains too.
The sixth ad is another generic auction website, not mentioning Houston anywhere.
Now look at the seventh and final ad. Its headline is exactly the keyword you as the consumer searched for. Plus, the ad description is speaking directly to you. The description is asking a question that you already know is yes. You already searched for houston auto auction, so you are indeed looking for information. It leads you to think the website has information regarding car auctions in Houston. Plus, it has a call to action, subconsciously persuading consumers to click the ad.
Which ad would you as the consumer click on?
You want good sales copy in the ad description to compel your consumers to click your ad. Not only will this drive traffic to your website, but it will give you a good CTR in Adwords. Remember that a good CTR is necessary to maintain your quality score.
Writing good sales copy is something you can do. The Google website search will often show you examples of good sales copy for the exact keywords you are trying to write for. The example above demonstrates that. You can modify the good sales copy you find on Google search for your own campaign.
Finally you have the link portion of your ad. You can also add your keywords to the display url. The display url is roughly one quarter of you total ad. Use the display url to your advantage. The display url domain must match the destination url domain, but other than that you can put anything you want in it. It's one more opportunity to display the keyword to the consumer, and convince them that your website is relevant. Use as much of the keyword as you can, limited to 35 characters in the display url. Back to the Buy Adwords example keyword, the display url can be mydomain.com/buy-adwords.
After you save your ad Google Adwords will retrieve the HTML of your URL. Adwords does this to determine your quality score and determine how much the minimum bid is. Since you have already created the highly relevant landing page for your keyword, Google will assign a good quality score. Adwords will likely allow you to bid as little as five cents per click.
CTR
You know CTR is the most important factor in the Adwords Quality Score. Now that you have the keyword, ad and landing page ready and running on Adwords you need to concentrate on your CTR.
Adwords allows the marketplace to determine the quality of ads. When you establish your campaign, Adwords scans your ad and landing page and assigns the quality score. Your ad begins to get impressions and clicks. This translates into the CTR. Google will adjust the quality score based on the CTR, allowing the marketplace to decide which are the better ads. Adwords assumes that if your ad is generating a high CTR, your ad must be relevant to the keyword. The human consumers find your ad compelling enough to click on it. Google adjusts your quality score higher because of the high CTR. A higher quality score may boost your ad position, resulting in more clicks and an even higher CTR. It becomes a cycle.
You should set a high Cost per Click (CPC) for the first two weeks. Relevance and initial Quality Score will reduce your cost, but you still want to a pay a premium for those first two weeks particularly in a competitive market. Why? Your goal during those two weeks is to get your CTR at least 5% and hopefully 10% or more. This is the good CTR you want to build. If you aren't in the top three positions and getting 5% CTR, you need to raise your CPC.
After two weeks with your CTR at 5% or better, check your quality score. At high CTR rates, the quality score will go up. If the quality score goes up, then you will instantly see lower CPCs due to Adwords auction system. Plus, you can begin to lower the CPC by 10% every week. You must monitor your campaign to make sure you keep the same CTR. Raise the CPC if you see the CTR go down.
Eventually, you will have a high CTR campaign with a low CPC.
Each ad group quality score is affected by the overall campaign CPC. If you have some adgroups or keywords that aren't performing well, move them to another campaign or delete them. You do not want poor perform keywords to damage your overall campaign.
Each month you should evaluate your campaign and delete ad groups and keywords with less than one half percent CTR. These keywords will be a drag on your entire campaign, increasing overall impressions but not adding CTR. Deleting these poor performing keywords will boost the overall CTR for your campaign, and allow you to maintain low bids.
Advanced Adwords Topics
You now have an Adwords ad and a landing page that are highly relevant to a particular keyword in your market. You will start getting traffic from Adwords as inexpensively as possible.
You can repeat this process for as many additional keywords you would like to build more traffic.
This concludes the discussion on Adwords, Quality Score and Relevance.
The next sections begin implementing and improving what has been covered. Most importantly, you'll learn how to use the tools here at imarketingtool.com to automate all the important tasks. You'll learn how to save time and effort during the labor intense parts.
Let's get started.
Review of Dynamic Keyword Insertion
{KeyWord: Local Auctions}
Find auto auctions & information
in Houston. Save thousands.
You may or may not know that Adwords includes a feature called dynamic keyword insertion. It's used in the advanced strategy. You use the token "{keyword: default text}" when creating your ad headline, description or destination url. When Google displays the ad, it will replace the token with the term the consumer searched for. Please see the example to the right.
The top ad on the right shows an example ad headline and two description lines. You'll notice the headline is simply the token "{KeyWord: Local Auctions}". This is token is replaced with the term the user searched on when the ad is displayed. That is not the keyword you are targeting (Adwords assumes you have more than keyword per Ad Group). When you use the strategy of one exact keyword match per Ad Group, there is no difference. The term searched for will be the keyword targeted. But, outside the strategy the distinction is important.
An Adwords headline can only contain 25 characters. You are allowed to extend the token in case the search term is more than 25 characters. If the search term has more the 25 characters, the default text is used. The default text is the portion of the token following the colon. In the top example, the default text is "Local Auctions".
Houston Auto Auction
Find auto auctions & information
in Houston. Save thousands.
The bottom ad is how Adwords will render the ad, assuming the consumer searched on "houston auto auction". When it is rendered, the token is replaced with the search term. Keep in mind that you can use the token in the description or destination url as well.
How you use or mix uppercase and lowercase in the token affects the display. Again, we'll use "houston auto auction" as the search term.
| Token |
Explanation / Display |
Display |
| {keyword: Local Auctions} |
lower case |
houston auto auction |
| {Keyword: Local Auctions} |
first word capitalized |
Houston auto auction |
| {KeyWord: Local Auctions} |
every word capitalized |
Houston Auto Auction |
Dynamic keyword insertion is particularly valuable when you have one exact match keyword per Ad Group. You know exactly what the searched term is. If you have multiple keywords or broad matched keywords, you will not be sure what the search term will be. You can find examples on Google of poor usage of the technique. The ads will not make sense, confuse consumers and result in poor click through rates (CTR).
You can read more about this topic form Google itself, at Google Support dynamic keyword insertion.
Next, you'll learn how to automate Adwords so you really can have one keyword per Ad Group and not have to do it by hand. Remember the concept of tokens, because you'll find it in the next section too.
Generating Campaigns
Your goal is to have a single campaign in Adwords with many Ad Groups, each targeting a single keyword or phrase. However, creating such a campaign is very tedious and time consuming. Here at imarketingtool.com you'll have access to a tool to help you automate creating such a campaign for whatever keywords you choose.
Google has released the Adwords Editor program. It is software written by Google that allows you to manage your Adwords account on your computer and then upload any changes to Google. One can imagine that the software is designed to reduce the bandwidth on the Adwords website. Instead of users managing their account on the internet, they do it on their own computers and only upload the changes. Imagine the reduction in traffic to the Adwords servers.
The Adwords Editor program allows you to backup and restore your entire account, or individual campaigns. You can share individual campaigns across multiple accounts using the export and import features of the Editor. Files exported from the Editor have an extension of ".aea" which stands for adwords editor archive file.
Using the imarketingtool.com tools, you'll be able to generate an Adwords Editor export .aea file. You then import this file into the Editor. Then simply upload the editor changes to Google. You have reduced several hours of work into a few minutes.
First you'll want to download the Google Adwords Editor. You'll want to learn how to use the Editor. Google has instructions and help available when you download the Editor. You be interested in the following three topics.
houston auto auction
houston car auction
philadelphia auto auction
philadelphia car auction
seattle auto auction
seattle car auction
...
Next you create the Editor .aea file using the imarketingtool.com Campaign Creator tool. You'll need your list of keywords. You may use as many keywords and phrases that you want. The tool expects the keywords in the same format as Adwords. That is, one keyword or phrase per line. Please see the example to the right.
The tool will create an Ad Group for each keyword, or a single Ad Group with all the keywords in it. You'll have the option to choose which campaign you prefer. You can choose broad, phrase or exact match for your keywords.
You'll also need to compose your ad. The tool will repeat the same ad across all the Ad Groups, so carefully construct your ad and make sure it works with keywords. Just as Adwords uses tokens, the tool supports tokens that will be translated when the ads are created. The token is a part of the ad that will be replaced with the specific keyword when the tool is run. This allows you to customize the Ads for each keyword.
| Token |
Replaced With |
| [keyword] |
the current lowercase keyword |
| [Keyword] |
the current keyword with the first character captialized |
| [KeyWord] |
the current keyword with the first character of each word captialized |
| [KEYWORD] |
the current uppercase keyword |
| [dash] |
the current lowercase keyword with dashes subsituted for spaces. This is useful for Url Rewriting. |
| [Dash] |
the current dashed keyword with the first character captialized |
| [DASH] |
the current uppercase dashed keyword |
There are few distinctions between Adwords tokens and the Campaign Creator tool tokens.
- The Campaign Creator tokens use square brackets "[]" instead of curly brackets "{}"
- The Campaign Creator tokens are the actual keyword, not the search term like Adwords tokens.
- The Campaign Creator tokens are converted when creating the .aea file, not when the ad is rendered
The Ad Headline should be the keyword or phrase in most situations, so use the [keyword] token or dynamic keyword insertion in the headline. In fact, the tool has the [keyword] token as the default.
The two lines of description may or may not contain tokens. It depends on your sales copy. Remember that your ad must have a good Click Through Rate (CTR) to maintain a Quality Score. Maintaining a good CTR depends on your sales copy. A CTR of three percent is good enough to maintain the Quality Score. If you are not getting three percent, you may need to adjust your sales copy. The Adwords Strategy Guide has a good discussion on what good sales copy is.
A suggested phrase is "Did You Know that (Keyword) Could (Insert Benefit)?". You could use the [keyword] token in the sentence to customize each ad.
You also know that using the keyword in the Adwords Destination will help your Quality Score. Again, Adwords will scan your landing page, such like Google Search scans pages. A highly relevant landing page will cause Google to rank you page as highly relevant to the keyword. So, Google will assign you a higher Quality Score. Several factors play into making a landing page relevant to a keyword, and the URL is one of them.
You can use the tokens in your Destination Url. For example, if your keyword is "Houston auto auction", your landing page should be named "houston-auto-auction.htm". Then you can set the Destination URL in the tool to "www.(your domain).com/[dash].htm".
In addition, you can use tokens or dynamic keyword insertion in your display url. This will display your keyword an additional time to the user in the ad, and may persuade them that your ad is relevant.
When you have your keywords and ad text in the tool, click the Generate button on the tool and you'll be able to download .aea file. The .aea file is an Adwords Editor archive file. Save the .aea file to you computer. Start the Adwords Editor program, and import your newly generated .aea file into the Editor.
You will now be able to edit your new campaign in the Adwords Editor. You can make any final adjustments if you wish. Next, you accept the new changes in the Editor. Finally, you post or upload your changes to Google. When that is complete you will have a new campaign in Adwords.
You can repeat this process for as many campaigns as you like, creating and importing multiple campaigns. To summarize, here are the steps to using the Editor and the tool.
- Download the Adwords Editor.
- Synchronize the Editor with Google Adwords and pull in your existing Adwords data.
- Visit the imarketingtool.comCampaign Creator tool.
- Customize your Campaign name, keywords, and ad text. Use tokens where appropriate.
- Generate and download your .aea file.
- Import the .aea file into the Editor.
- Accept the changes in the Editor.
- Post the changes to Google.
- To repeat, go back to step three.
Use of the imarketingtool.com Campaign Creator tool is included with your purchase. Simply visit the link above. You will be required to login, and after you login just visit the Campaign Creator tool.
Better than Dynamic Keyword Insertion
The tokens the above tools provide are superior to dynamic keyword insertion. There are several reasons why this is true.
First, the tool tokens are replaced as the tools are run. The generated output that is posted to Adwords will only have static text. The ad will fulfill the quality score requirement of having the keyword in the ad text. Dynamic keyword insertion, in its tokenized form, means that your ad will not contain the keyword. So, your quality score will be better with the tool tokens.
Second, the tool tokens are replaced with your keyword and not the consumers search term. The consumers search term is an unknown (unless you have only the exact match keyword in your ad group). You really don't know what Adwords will be inserting. But the tool tokens are replaced with your keywords. You know what each keyword is, you supplied the list. You can safely construct your ad knowing what each token will be replaced with.
What does this mean? You should stick to the one Ad Group per keyword strategy for your primary keywords. When you use the tool tokens, your keyword will get placed in the ad text, and you'll control exactly what the ad says. It'll be plain old regular text when you post it to your Adwords account.
Keyword Revelance Versus Sales Copy
A landing page has two goals. One, provide a high quality score to Adwords by being revelant to the keyword. Two, convert the visitor who clicked the Adwords ad into a sales. These two goals are often at odds. A paragraph designed to get a high quality score is not like to convert. Conversely, a media rich sales letter is not going to get a high quality score. How do you achieve both goals in a single generated landing page? This is the biggest hurdle in generating landing pages.
The solution is very simple. Don't try to do both at the same time.
Create your sales letter or pitch page. The sales letter is pure sales copy. It is designed with only one goal, to convert a visitor into a sale.
Next, create your landing pages. The landing page has only one goal, get a high quality score from Adwords (and the Search Engine as well). The Adwords Strategy Guide explained in detail how to create a landing page. The major relevancy points are listed below.
- The domain the page resides on
- The filename of the page
- The title of the page
- The page meta tags
- The content in <h1> tags
- The content of the page
Now that you have both pages, simply put the sales letter in an iframe tag at the top of the landing page.
To your visitor, the iframe content will appear first. This is the sales letter, compelling them to convert. The keyword rich content is pushed down below the fold. The fold is the point on a page where a visitor must scroll down to read more. This keyword rich content can be well beyond the fold depending on how high you make your iframe.
To the Google robots, the iframe is just a single html tag. The robots go immediately to the next part of the page, your keyword rich content. The robots will parse the sales letter as part of your website, but it's content will not be counting toward the landing page.
In the end you have two pages, one sales letter and one landing page. Each page has a specific goal. Adwords will send traffic to the landing page. And thanks to the iframe, the visitor will see the sales copy.
Using 404 Error Pages for Url Rewriting
The best way to describe Url Rewriting is to give an example of url rewriting with a 404 error page. When you type in a url for page that doesn't exist on your website, the web server responds with "404 error". 404 is the standard code for a page not found error.
Both Microsoft IIS and Apache web servers allow you have a custom 404 error page. This means you can design you own custom error page and display it every time there is a 404 error. Imagine creating a new 404 error page with server side scripting logic (PHP, ASP.NET or whatever). The logic of the page can determine what the url caused the error. The logic could then derive the keyword from the page name and redirect to your generic landing page.
In a nutshell, that's what happens with all methods of url rewriting. You intercept a request url for page that doesn't exist and redirect it to a page that does exist. The consumer, Google search engine and Google Adwords won't know the page has been redirected, or rewritten.
What does this means of us as Adwords marketers? It means we can dynamically generate pages for any keyword. All we need to do is setup url rewriting and then decide what to render.
Custom error pages are earliest and easiest form of url rewriting. But today we have more options, and those options don't require changing the web server configuration for custom error pages. Let's look at the modern way to accomplish url rewriting.
PHP Url Rewriting
Url Rewriting in PHP is a snap. It's a simple two step process.
- Modify the .htaccess file in the root folder of your website. You'll add instructions to send non-existent pages to your dynamic landing page. It's 5 lines of code that you can cut and paste.
- Create your dynamic landing page.
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^([^/]+).php?$ urlrewrite.php?keyword=$1 [L]
You can download the code which shows you what changes to make to the .htaccess file. It also contains a sample landing page which dynamically generates content for any keyword. You can install this on your PHP website in fifteen minutes and start rewriting urls.
First, you need to turn on rewriting in your .htaccess file. At the root folder of your PHP website, either create a .htaccess file or modify an existing one. You will most likely have an existing .htaccess file. You can simply paste the code at the bottom of an existing file.
Here is the line by line explanation of these modifications.
| Code |
Description |
| RewriteEngine On |
Instructs the server to turn on Url Rewriting |
| RewriteBase / |
Begin checking for non-existent urls in the root folder |
| RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f |
Apply rewriting to any url pointing to a file that doesn't exist |
| RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d |
Apply rewriting to any url pointing to a directory that doesn't exist |
| RewriteRule ^([^/]+).php?$ urlrewrite.php?keyword=$1 [L] |
A regular expression of what to rewrite and what page to redirect to. Here any request ending .php is rewritten. All rewrites are send to a page named urlrewrite.php. In addition, a querystring parameter named keyword is sent ot urlrewrite.php and it contains the requested page name. |
This code essentially says look for any non-existent file, and according to the last line, if it ends in .php extension, redirect it to urlrewrite.php with the filename before the .php extension as a querystring parameter. This last part is important. You will want the filename portion of your destination url to be the keyword ( Google will recognize the keyword and boost the quality score). So, the filename is the keyword. You need to know what the keyword is when you reach urlrewite.php, and last why the querystring parameter is present. All you need to do on the urlrewrite page is check the keyword querystring parameter and you'll know what the keyword is.
For example, imagine your keyword is "football". You can create a url for the keyword.
http://www.MyDomain.com/football.php
Don't worry that page football.php doesn't exist on your website. In fact, this is exact the situation you want to have. The Url Rewrite Engine realizes that page football.php doesn't exist, so it redirects the url to urlwrite.php. Plus, it takes the page name "football" and makes it the keyword parameter.
http://www.MyDomain.com/urlrewrite.php?keyword=football
This rewriting happens behind the scenes at the server. To the consumer, and Google Search Engine and Google Adwords, the original, keyword rich url is the only url they see. It will look like you have multiple pages when you really only have one.
You will often have two or more words in a keyword, and therefore spaces in your page name. Spaces are not valid characters in the Url. The browser must encode spaces in the urls since spaces are invalid character. Spaces will translated into "%20". The browser will do this automatically. For example, take the keyword "football tickets".
http://www.MyDomain.com/football%20tickets.php
The Adwords Editor will not accept invalid urls. You have two options when dealing with spaces in keywords. One option is to properly encode the Urls in either the Adwords Editor or the web based interface. The Campaign Creator will automatically encode spaces to make sure data imported in the .aea file is valid.
The other option is to replace spaces with dashes in the page name. A page name with dashes will pass a dashed keyword to the urlrewrite.php landing page. The urlrewrite.php must replace the dashes with spaces to get back to the original keyword. This is already done in the code in the zip file. Dashes also have the benefit of begin more readable.
http://www.MyDomain.com/football-tickets.php
Next we have the code for the urlrewrite.php itself.
<?php
// establish a keyword variable and set it to a default
$myKeyword = "default";
// check for "keyword" querystring parameter
if (isset($_GET['keyword']))
{
// if found, put the value in the variable
$myKeyword = preg_replace("/-/", " ", $_GET['keyword']);
// replace dashes with spaces
$myKeyword = str_replace("-", " ", $myKeyword);
// make the first letter of each word in the keyword capitalized
$myKeyword = ucwords(strtolower($myKeyword));
}
?>
<html>
<head>
<title><?php echo $myKeyword; ?></title>
<meta name="keywords" content="<?php echo $myKeyword; ?>"/>
<meta name="description" content="<?php echo $myKeyword; ?>"/>
...
</head>
<body>
<h1><?php echo $myKeyword; ?></h1>
...
</body>
</html>
Here, you have the PHP page getting the keyword from the querystring parameter. If the keyword is found, the first letter of each word in the keyword is capitalized. Finally, the keyword is substitution throughout the page in the page title, meta tags and heading tags.
In Adwords, you create the destination url. With Url Rewriting you simply make the destination url the keyword. For example, if your keyword is "soccer", you make your destination url point to "soccer.php".
http://www.MyDomain.com/soccer.php
This accomplishes two things. First, since your Adwords keyword is "soccer", you want your landing page to dynamically generate content for "soccer". You learned the Url Rewrite Engine gets the keyword from the page name. So in order to pass "soccer" to the urlrewrite.php your page must be soccer.php.
Second, the destination url now contains the keyword. Adwords considers the page name when assigning relevance and Quality Score. By using the keyword in the destination url, you will boost your Quality Score.
Adwords will visit your page. Behind the scenes, the request will be sent to urlrewrite.php. Urlrewrite.php will generate content targeted to the keyword soccer. Adwords will still see the soccer.php url, and it will see the content relevant to soccer. You will get credit for a relevant landing page.
You just put your marketing message, be it a sales letter or an opt-in form, on the urlrewrite.php. When a consumer clicks your ad, they get sent to the rewritten page, tailored for the keyword and also containing your marketing message.
You can create any number for destination urls you want, for whatever keywords you want. Each url will be rewritten to the same dynamically generated page. You will have what appears to be dozens of pages when you really only have one.
You can download the code for both the .htaccess file and a sample landing page, urlrewrite.php. You want to modify the urlrewrite.php to contain your message.
ASP.NET Url Rewriting
Url rewriting in ASP.NET is accomplished through the use of an HttpModule. An HttpModule class can be created by simply extending the System.Web.IHttpModule class. The UrlRewrite class does just that and adds an event handler for the Application_BeginRequest method.
You may download the compiled ASP.NET 2.0 DLL in the AmtDll.zip file. The DLL contains the UrlRewrite class in the AMT namespace. You may download the C# Source code for the DLL in the AmtSource.zip file.
The DLL will go in the bin folder of your website. You need to modify the web.config to use the HttpModule. The web.config code is below.
<configuration>
<system.web>
<!-- required for URL Rewriting -->
<httpModules>
<add name="UrlRewrite" type="AMT.UrlRewrite,AMT"/>
</httpModules>
</system.web>
</configuration>
In addition, the class requires a few AppSettings.
| Key |
Value |
Description |
| UrlRewrite_Config |
~/UrlRewrite.config |
A config file that contains a regex to evaluate against the url to check for rewriting. |
| UrlRewrite_SearchResults |
~/SearchResults |
A folder to cache the xml if you choose to generate content for your page. |
| UrlRewrite_XSL |
~/urlrewrite.xsl |
The XSL Transform to conver the cached xml into html. |
| UrlRewrite_GoogleApiKey |
ABC |
Your Google Search API key should you choose to generate content. |
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="UrlRewrite_Config" value="~/UrlRewrite.config"/>
<add key="UrlRewrite_SearchResults" value="~/SearchResults"/>
<add key="UrlRewrite_XSL" value="~/urlrewrite.xsl"/>
<add key="UrlRewrite_GoogleApiKey" value="ABCX"/>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
The HttpModule requires a config file to provide a regular expression telling what urls to rewrite. This provides the flexibility to send different urls to different pages. The following table describes the attributes and code below will rewrite any non-existant urls.
| Attribute |
DataType |
Description |
| IncludeQueryString |
bit (0/1) |
Flag to include the original QueryString when rewriting |
| Pattern |
regex / string |
The regex to check the original url to see if it should be rewritten. |
| RewriteUrl |
url / string |
The url of the landing page to redirect to. |
<Configuration>
<Rule IncludeQueryString="1" Pattern="[A-Za-z0-9/]+.aspx" RewriteUrl="~/urlrewrite.aspx" />
</Configuration>
Last, you need a page to send the non-existant urls to. The HttpModule will send the keyword in the "urk" QueryString parameter. The keyword is derived from the page name. For example, if the url is "http://www.mydomain.com/car-auction.aspx" the keyword will be "car auction".
You may download the website source in the website1.zip file. This website has a web.config, a urlrewrite.config and urlrewrite.aspx landing page.
PHP Dynamic Relevant Content
So far you've learned how to setup url rewriting and dynamically generate pages. You've put the keyword in the title, the meta tags and the heading tags. This starts you on the path to a relevant landing page. You also learned how to put your sales letter in a iframe on your page so that the consumer sees your sales copy.
But what about dynamically generating relevant content? You could have generic HTML on your dynamically generated landing and place the keyword throughout the content. But we can do better than that.
The Google Search API allows us to query the Google Search engine for a keyword and get the first 8 links. The API returns the first 8 results with the url, the url text and brief description of the link. Here is the PHP code for calling the API.
function GoogleSearchWithKey($apiKey, $keyword)
{
$format = "http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/services/search/web?v=1.0&q=%s&key=%s&rsz=large";
$url = sprintf($format, urlencode($keyword), $apiKey);
$ref = "http://localhost/test";
// sendRequest
// note how referer is set manually
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_REFERER, $ref);
$body = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
// return JSON object
return json_decode($body);
}
Simply include this code on the dynamically generate page to get the Google Search Results from the API. Then translate it into HTML and render it on your page. Now you have dynamically generated, keyword relevant content on your page that is unique to the keyword.
Google allows you to call the API with or without an API key. The only trouble in using it without a key is that Google may temporarily block traffic from your website if the volume of requests exceeds a limit they've set. Now imagine that every time a consumer clicks your Adwords Ad (or the googlebot visits) you make a call to the API. It is easy to exceed the limit of requests.
One simply way to prevent exceeding the limit is to cache the search results after you make the API call. All you do is save the HTML to a file on the server after you call the API. Then whenever the page is dynamically rendered you first check for a cached file and use the HTML from it. This way the API is only called one time for each keyword and you prevent making mutliple calls for the same keyword.
Of course, you could also just sign up for an API key. API calls made with a key are not blocked. You can call the API as much as you want. You may still want to cache the results even if you use an API key. There's no sense making unnecessary calls to Google when we can cache the results. You may apply for an API key at the following link. http://code.google.com/apis/ajaxsearch/signup.html.
Now you have dynamically generated page with keyword relevant content. The full source code of the PHP landing page is below. It is well commented if you want to see the technical details. If you want to see an example of this code in use, please visit http://adwords.qupis.com/philadelphia-car-auction.php.
<?php
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* This is the landing page for url rewritten pages.
* the HTACCESS will direct non-existant urls to this page
* and supply the page name (ex.: college-football.php) as
* the "keyword" querysting (ex.: ?keyword=college-football)
*
* This page performs the following actions
* 1. read the keyword from the querystring
* 2. dynamically generate page with the keyword in the title,
* meta tags, heading, etc.
* 3. load a sales letter page in a iframe tag to that the
* sales letter is the first thing seen by the visitor
* 4. generate relevant links and text from the Google Search
* API (or cached on the server) and display on page
*
* You must edit the variables below
*
* name type description
*
* $myApiKey string HexaDecimal Google API key.
* Apply at http://code.google.com/apis/ajaxsearch/signup.html
* if you don't have an API key, leave as empty string.
* API key is recommended.
*
* $myIframeUrl string Url of the sales page to load in the iframe (you may use Clickbank hoplink).
*
* $myIframeHeight string Height of the iframe ("2000" is usually a good height).
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
$myApiKey = "";
$myIframeUrl ="http://scrptcal.gt4idiots.hop.clickbank.net";
$myIframeHeight ="200";
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Not necessary to edit the PHP code after this point
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
$myKeyword = GetKeyword("");
$myHtml = Main($myApiKey, $myKeyword);
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Main processing
*
* parameters
* name type description
* $apiKey string HexaDecimal Google API key
* $keyword string the keyword
*
* ouptut
* type description
* string HTML text
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function Main($apiKey, $keyword)
{
$dash = str_replace(" ", "-", $keyword);
// check for cached file
$cacheFolder = "SearchResults";
PHPCreateFolder($cacheFolder);
$cacheFile = $cacheFolder . "/" . $dash . ".xml";
$html = PHPReadFile($cacheFile);
if (strlen($html) == 0)
{
// no cached file exists, so get Google Search Results
// fetch the Google results
if (strlen($apiKey) == 0)
{
$json = GoogleSearch(array('q' => $keyword,'rsz' => 'large'));
}
else
{
$json = GoogleSearchWithKey($apiKey, $keyword);
}
//print_r($json);
// parse JSON object into HTML
$html = ParseJson($json);
//echo $html;
// cache the HTML on the server
PHPSaveFile($cacheFile, $html);
}
return $html;
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Get the keyword from the querystring (HTACCESS puts keyword in querystring
*
* parameters
* name type description
* $default string default keyword to use if no keyword in querystring (should not happen)
*
* ouptut
* type description
* string the keyword
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function GetKeyword($default)
{
$result = $default;
// check for "keyword" querystring parameter
if (isset($_GET['keyword']))
{
// if keyword found, put the value in the variable
$result = preg_replace("/-/", " ", $_GET['keyword']);
// replace dashes with spaces
$result = str_replace("-", " ", $result);
// make the first letter of each word in the keyword capitalized
$result = ucwords(strtolower($result));
}
return $result;
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Translate JSON object to HTML string
*
* parameters
* name type description
* $json object JSON object
*
* ouptut
* type description
* string HTML text
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function ParseJson($json)
{
$result = '<div class="searchresults">';
foreach($json->responseData->results as $gres)
{
$format = '<div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow" href="%s">%s</a><br/>%s</div>';
$html = sprintf($format, $gres->url, $gres->title, $gres->content);
$result = $result . $html;
}
$result = $result . '</div>';
return $result;
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Query Google AJAX Search API
*
* example call
* $json = google_search_api(array('q' => $keyword,));
* print_r($json);
*
* parameters
* name type description
* $args array URL arguments. For most endpoints only "q" (query) is required.
* $referer string Referer to use in the HTTP header (must be valid).
* $endpoint string API endpoint. Defaults to 'web' (web search).
*
* ouptut
* type description
* object JSON object
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function GoogleSearch($args, $referer = 'http://localhost/test/', $endpoint = 'web')
{
$url = "http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/services/search/".$endpoint;
if ( !array_key_exists('v', $args) )
$args['v'] = '1.0';
$url .= '?'.http_build_query($args, '', '&');
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
// note that the referer *must* be set
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_REFERER, $referer);
$body = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
//decode and return the response
return json_decode($body);
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Query Google AJAX Search API
*
* documentation:
* http://code.google.com/apis/ajaxsearch/documentation/
*
* parameters
* name type description
* $apiKey string HexaDecimal Google API key.
* $keyword string keyword to return data for
*
* ouptut
* type description
* object JSON object
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function GoogleSearchWithKey($apiKey, $keyword)
{
$format = "http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/services/search/web?v=1.0&q=%s&key=%s&rsz=large";
$url = sprintf($format, urlencode($keyword), $apiKey);
$ref = "http://localhost/test";
// sendRequest
// note how referer is set manually
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_REFERER, $ref);
$body = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
// return JSON object
return json_decode($body);
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* File I/O functions
* for caching search results HTML on the server
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function PHPReadFile($file)
{
$result = "";
if (file_exists($file))
{
$result = file_get_contents($file);
}
return $result;
}
function PHPSaveFile($file, $data)
{
$file_ptr = fopen($file, "w");
fwrite($file_ptr, $data);
fclose($file_ptr);
}
function PHPCreateFolder($folderName)
{
if (file_exists($folderName))
{
// folder already exists
}
else
{
mkdir($folderName, 0777);
}
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* Miscellanous function
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
function WriteLn($data)
{
echo "<div style='background-color: #ffcc00;'>";
echo $data;
echo "</div>";
}
/*
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
* End PHP Code
* Begin HML Code
* ********* ********* ********* ********* *********
*/
?>
<html>
<head>
<title><?php echo $myKeyword; ?></title>
<meta name="keywords" content="<?php echo $myKeyword; ?>, second static
keyword, third static keyword"/>
<meta name="description" content="<?php echo $myKeyword; ?> information
at MyWebsite.com. Find everything you need to know about
<?php echo $myKeyword; ?>."/>
<style>
body { background-color: #e0e0e0; margin: 0; }
h1 { font-size: 12pt; color: #000000; text-align: center;}
.MainContent { padding: 10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src="<?php echo $myIframeUrl; ?>"
height="<?php echo $myIframeHeight; ?>"
width="100%" border="0" scrolling="no">
</iframe>
<div class="MainContent">
<h1><?php echo $myKeyword; ?></h1>
<?php echo $myHtml; ?>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of HTML rendered by the page. It is for the keyword College Football. Notice
how the page is targeted to the keyword and the content is relevant.
<html>
<head>
<title>College Football</title>
<meta name="keywords" content="College Football, second static keyword,
third static keyword"/>
<meta name="description" content="College Football information at
MyWebsite.com. Find everything you need to know about College Football."/>
<style>
body { background-color: #e0e0e0; margin: 0; }
h1 { font-size: 12pt; color: #000000; text-align: center;}
.MainContent { padding: 10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src="http://www.google.com" height="500" width="100%" border="0"
scrolling="no"></iframe>
<div class="MainContent">
<h1>College Football</h1>
<div class="searchresults"><div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://espn.go.com/college-football/">NCAA <b>College Football</b> Teams,
Scores, Stats, News, Standings <b>...</b></a><br/>Get the latest NCAA
<b>college football</b> news, scores, stats, standings, and more on ESPN.com.
</div><div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://www.ncaafootball.com/">NCAAFootball.com :: Where Every Game Counts</a>
<br/><b>college football</b>, ncaa football, football, college, top25, BCS,
NCAA, Division I , Division I-AA, Division I Bowl Subdivision, Division I Championship
<b>...</b></div><div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://cfn.scout.com/"><b>College Football</b> News Front Page</a>
<br/>Oct 13, 2010 <b>...</b> CollegeFootballNews.com covers <b>college
football</b> on the Scout.com Network.</div><div class="searchresult">
<a rel="nofollow" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/College_football"><b>College
football</b> - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia</a><br/><b>College
football</b> refers to American football played by teams of student athletes fielded
by American universities, colleges and military academies. <b>...</b></div>
<div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://sportsillustrated.cnn.com/football/ncaa/">NCAA Football news, scores, rankings
- <b>College Football</b> - SI.com</a><br/>Find NCAA football breaking
news, scores, stats, rankings, polls, truth and rumors and <b>college football</b>
analysis from Sports Illustrated at SI.com.</div><div class="searchresult">
<a rel="nofollow" href="http://www.collegefootball.org/"><b>College Football
</b> Hall of Fame</a><br/>Located in South Bend, Indiana. Trivia questions
with prizes, polls, voting for Hall of Fame nominees, Hall information, and Featured
Famers.</div><div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://rivals.yahoo.com/ncaa/football"><b>College Football</b> on
Rivals.com - NCAA Football, NCAAF News, Scores <b>...</b></a>
<br/>Complete <b>College Football</b> news, scores, standings.</div>
<div class="searchresult"><a rel="nofollow"
href="http://www.sportingnews.com/ncaa-football">NCAA <b>Football</b> - Sporting
News</a><br/>Anarchy continues to reign in <b>college football</b> as
No. 1 falls for the second straight week. Wisconsin takes down Ohio State in raucous Camp
Randall, 31-18. <b>...</b></div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
You can download the code for both the .htaccess file and a sample landing page, urlrewrite.php.
ASP.NET Dynamic Relevant Content
You can dynamically generate content in ASP.NET as well. You make the same call to the Google Search API in .NET and display the results on the page.
The SearchResults class in the AMT DLL will call the Google Search API and cache the xml for future use. You can call the methods of this class to create content for any keyword.
You may download the compiled ASP.NET 2.0 DLL in the AmtDll.zip file. The DLL contains the UrlRewrite class in the AMT namespace. You may download the C# Source code for the DLL in the AmtSource.zip file. You may download the website source in the website1.zip file. The urlrewrite.aspx landing page demonstrates how to use the SearchResults class.
Landing Page Generator
If you don't have PHP or ASP.NET hosting for you website, you cannot use url rewriting to dynamically generate landing pages. Instead, you will need static landings for each keyword. The landing page generator tool creates these static pages.
The landing page generator creates files for use on your website. The basic instructions are below.
- Cut & Paste your list of keywords
- Select the file extension you would like for your pages. This can be Html, ASPX, JSP or PHP.
- Customize the content template. This template will be customized for each keyword. You place tokens in the template where you want the keyword to appear.
- Click the generate button to download a zip file containing all your file plus a sitemap page.
Each keyword will have it's own landing page. The landing page will be the keyword itself with the selected extension. This uses the keyword in the filename of the page.
For example, imagine your keyword is "football". You can create a url for the keyword.
http://www.MyDomain.com/football.php
There is an example content template loaded in the page generator when you view the page. The template uses the strategy of a Sales Letter inside an iframe at the top of the landing page.
The content template also uses keyword tokens in the following places on the page.
- The title of the page
- The page meta tags
- The content in <h1> tags
- The content of the page
The tokens you may use in the content template are listed below.
| Token |
Replaced With |
| [keyword] |
the current lowercase keyword |
| [Keyword] |
the current keyword with the first character captialized |
| [KeyWord] |
the current keyword with the first character of each word captialized |
| [KEYWORD] |
the current uppercase keyword |
| [dash] |
the current lowercase keyword with dashes subsituted for spaces. This is useful for Url Rewriting. |
| [Dash] |
the current dashed keyword with the first character captialized |
| [DASH] |
the current uppercase dashed keyword |
There on several places on the provided content template that you will want to customize for your website.
| Area/Item |
Modification |
| Keyword Meta Tag |
Add additional static keywords to the meta tag. It is recommended that you leave the first keyword the "[KeyWord]" token. The token is replaced with the keyword. |
| Description Meta Tag |
Modify the description to be 3 or 4 sentences about your overall website. |
| iframe src attribute |
Modify the Iframe "src" attribute to be the url of your sales letter. |
| iframe height attribute |
The height of the iframe controls far down the visitor must scroll to see your content. 3000 or 3500 are recommended. |
| content |
Modify with 3 or 4 paragraphs regarding your market. Be aware of places you can substitute keywords, and change them to tokens. The more times your keyword appears in the content (while still being natural content), the higher the quality is. |
| contact us |
Modify the contact us and privacy policy hyperlinks to point to the correct pages |
| Analytics Code |
Edit with you Analytics code or delete the Analyatics code |
In addition, a LandingPage.css and sitemap.html file are included in the resulting zip file. The stylesheet allows you to customize the look of the html elements across all the generated pages from single point. The default content template imports this CSS file in the header.
The sitemap.html file is a hyperlinked list of the generated pages. You may use this as a sitemap, or you can cut & paste the links into your own sitemap page.
The Keyword Bracket Tool
The next tool you'll have access to is the Adwords bracket tool. One function of this tool is to wrap your keywords in the appropiate demlimiters for phrase, exact and negative matches. Keep in mind that the campaign builder tool will create a campaign with the proper matches, so you don't have to worry about it.
A very useful function of the keyword bracket tool is the ability to combine keyword lists. For example, imagine your keywords are "table" and "chair". You could have an additional set of keywords like "oak" and "maple". These keywords are modifiers or prefixes of your main keywords. The end result would combining all prefixes and keywords, demonstrated in the table below.
- oak table
- oak chair
- maple table
- maple chair
Imagine doing the same thing with geographic locations. For example, suppose your main keywords are "attorney" and "lawyer". You could major metropolitan cites as the modifiers or prefixes, like "New York", "Boston", and "Chicago". Combining these lists results inthe following.
- New York attorney
- Boston attorney
- Chicago attorney
- New York lawyer
- Boston lawyer
- Chicago lawyer
The tool includes lists of major metropolitan cities and states that you can use as prefixes with the touch of a button.
In addition, the keyword bracket tool allows you to create keyword level CPCs and Destination Urls.
When you add keywords to an ad group, you can include additional information like a Max CPC and Destination URL for the keyword. The format of such keyword is...
keyword ** MaxCPC ** DestinationURL
You are also allowed to omit the MaxCPC if you wish, and have...
keyword ** DestinationURL
For example, you could have...
MyKeyword ** http://www.MyDomain.com/LandingPage.aspx
The tool allows you to generate the keyword list in this syntax. You can use the same tokens from the campaign creator to generate unique destination urls.
Putting it all together
In the previous sections, you learned how to use url rewriting in a variety of languages to display a page other than what is in the url. You also learned how to make a single page generate targeted content for any keyword. Now you simply put all the pieces together.
- Compose a keyword list.
- Use the Campaign Creator tool to create a campaign with one ad group per keyword. Using the tokens provided by the tool you can put the individual keywords in the ad headline and text. use the tokens to make unique destination url for each keyword that has the keyword as the page name.
- Generate a landing page for each keyword by implement a method of url rewriting. Alternatively, you may create static pages with the Landing Page Generator.
You eliminate all the manual labor from the process when you follow these steps. You generate your Adwords campaign instead of doing it by hand. You generate hundreds of Landing Pages automatically for your keywords. Or you create a single generic landing page with url rewriting instead of spending hours writing individual pages.
Conclusion
You now have the knowledge and tools to expand upon the Adwords Strategy.
- A solid strategy for making a campaign of multiple Ad Groups each containing only one specific keyword combined with url rewriting and a single targeted landing page.
- The Campaign Creator tool to automate the creation of your Adwords campaigns. This saves you time and effort when compared to generating campaigns by hand.
- The Adwords Bracket tool to automate the creation of your Adwords keywords.
- The code for constructing url rewriting system capable of redirecting traffic to your generic landing page. Download the PHP code.
- The code for producing targeted content for any keyword. Download the PHP code.
You will be able to create successful Adwords campaigns for any market and set of keywords using the techniques presented here. Your Ads will have good or great Quality Scores, allowing you to keep you maximum bids as low a possible. This will reduce your Adwords spending, but still generate high traffic for your website. Plus, you'll save yourself all the tedious and time consuming tasks of creating campaigns and landing pages manually.